
SQL Saturday 97 Slides and Code – EXCEPT, INTERSECT, APPLY
Download my slides and source code from my SQL Saturday 97 presentation. Continue reading SQL Saturday 97 Slides and Code – EXCEPT, INTERSECT, APPLY
Browsing Tag

Download my slides and source code from my SQL Saturday 97 presentation. Continue reading SQL Saturday 97 Slides and Code – EXCEPT, INTERSECT, APPLY
We are all familiar with seeing our data in a vertical format from SSMS. Here is a sample:
SELECT * FROM #EmployeeJobs Employee_ID Job_id 100 500 100 501 100 502 100 503 100 504 191 501 191 502 191 503 191 505 188 503 188 504 |
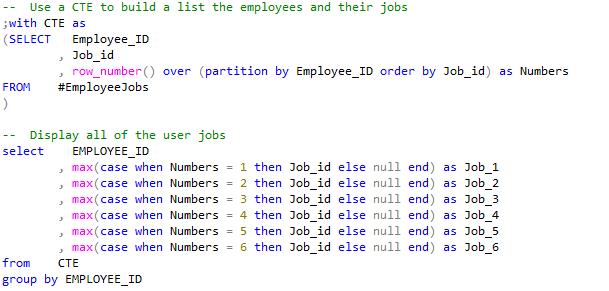
But what if you, or your customer want’s the data horizontally? That is easy enough with a CTE. Continue reading “Display results Horizontally in SQL Server”
Thanks to the team at TechRepublic.com and BOL, I have used CTEs to delete duplicates with ease in SQL Server 2005 and higher. Learn more about CTEs at TechRepublic. Here meat of the article a sample: ;WITH SalesCTE(Product, SaleDate, SalePrice, Ranking) AS (SELECT Product , SaleDate , SalePrice , Ranking = DENSE_RANK() OVER(PARTITION BY Product, SaleDate, SalePrice ORDER BY NEWID() ASC) FROM SalesHistory ) DELETE FROM SalesCTE WHERE Ranking > 1 Very easy and handy! Check out BOL for all kinds of information regarding Dense_Rank(), NEW_ID(), and PARTITION BY. While you’re there, check out RANK(), NTILE(), and ROW_NUMBER() I’m sure … Continue reading Common Table Expressions (CTE) in SQL Server 2005 and Up